Global Markets Recap - Week of July 17, 2023

1. What Moved the Markets?
Europe
European stocks had a positive week, driven by hopes of slowing inflation leading to a potential end to monetary policy tightening. Major Continental stock indexes also rose, with Italy's FTSE MIB up 0.67%, France's CAC 40 Index up 0.79%, Germany's DAX up 0.45%, and the UK's FTSE 100 Index surging 3.08%, partly due to the weaker British pound. European government bond yields declined as inflation cooled in the US and the UK, indicating expectations of a potential pause in monetary policy tightening. In the UK, annual consumer price growth slowed to 7.9% in June, exceeding expectations and aligning with the Bank of England's forecast. The eurozone economy avoided a recession, with revised figures showing flat GDP growth in the first quarter. The European Central Bank's leading hawks (Dutch central bank governor Klaas Knot and Bundesbank chief Joachim Nagel) indicated a more cautious stance on future rate hikes, given the plateauing of core inflation and the dependency on incoming economic data for decisions beyond July.
US
US equity indexes rose in hopes of avoiding a hard landing due to a tight labor market and moderating inflation. Nasdaq Composite saw a modest pullback. Value stocks outperformed growth in Russell 1000. Retail sales increased 0.2% in June, below the 0.6% consensus estimate. Jobless claims declined, reaching May's lowest level. U.S. Treasury Secretary Janet Yellen is optimistic about the economy, saying she does not expect a recession due to a resilient labor market and slowing inflation. However, the Conference Board's Leading Economic Index declined for the 15th consecutive month in June, indicating economic weakness linked to consumer sentiment, new orders, and housing construction slowdown. Bond investors anticipated a Fed rate hike, inverting yield curve. During the week, two-year U.S. Treasury note yields rose, while the benchmark 10-year U.S. Treasury note yield remained mostly unchanged. This led to an inverted yield curve, as investors anticipated another Federal Reserve rate hike at the central bank's July 25-26 policy meeting. The tax-exempt municipal bond market showed positive momentum, driven by reinvestments and strong demand for new deals. Investment-grade corporates showed solid demand, oversubscribing new issuance. Overall, cautious optimism with mixed economic indicators and bond market activity.
Japan
Japan's stock markets had mixed performance, with the Nikkei 225 Index falling 0.3% and the TOPIX Index gaining 1.0%. Investor caution ahead of the Bank of Japan's (BoJ) monetary policy meeting and a dampening of expectations regarding tweaks to the yield curve control framework influenced sentiment. A hot June core consumer price inflation print added pressure on the BoJ to tighten policy and raise inflation forecasts.
The 10-year Japanese government bond yield rose slightly to 0.48% from 0.47% the previous week, while the yen weakened against the U.S. dollar, reaching around JPY 141.82 from about JPY 138.76.
The Japanese government revised down its economic growth forecast for the current fiscal year to 1.3% but raised its total consumer price inflation forecast for 2023 to 2.6%. In June, Japan's core consumer price index rose 3.3% year on year, in line with expectations.
BoJ Governor Kazuo Ueda's comments dampened expectations of monetary policy normalization, emphasizing the need to achieve the 2% inflation target sustainably. The BoJ will review progress toward this target at each policy meeting, given its continued ultra-loose monetary policy under YCC.
China
Chinese equities faced a retreat as economic data pointed to slowing growth. The Shanghai Stock Exchange Composite Index fell 2.16%, while the CSI 300 declined 1.98%. In Hong Kong, the Hang Seng Index dropped 1.74%.
Year-over-year, China's GDP expanded 6.3% in Q2, faster than Q1's 4.5% growth but below expectations. On a quarterly basis, the economy grew 0.8%, down from Q1's 2.2% expansion, reflecting underlying growth better due to last year's pandemic lockdown. Unemployment held steady at 5.2%, but youth unemployment surged to a record 21.3%.
The government aims to boost corporate confidence by improving conditions for private businesses amid the struggling recovery. Additionally, Chinese authorities introduced an 11-point consumption plan to stimulate household spending.
China's real estate sector showed signs of weakness, with new-home prices remaining unchanged and property investment declining by 7.9% in the January-to-June period. These trends are attributed to poor consumer sentiment and deflationary pressures.
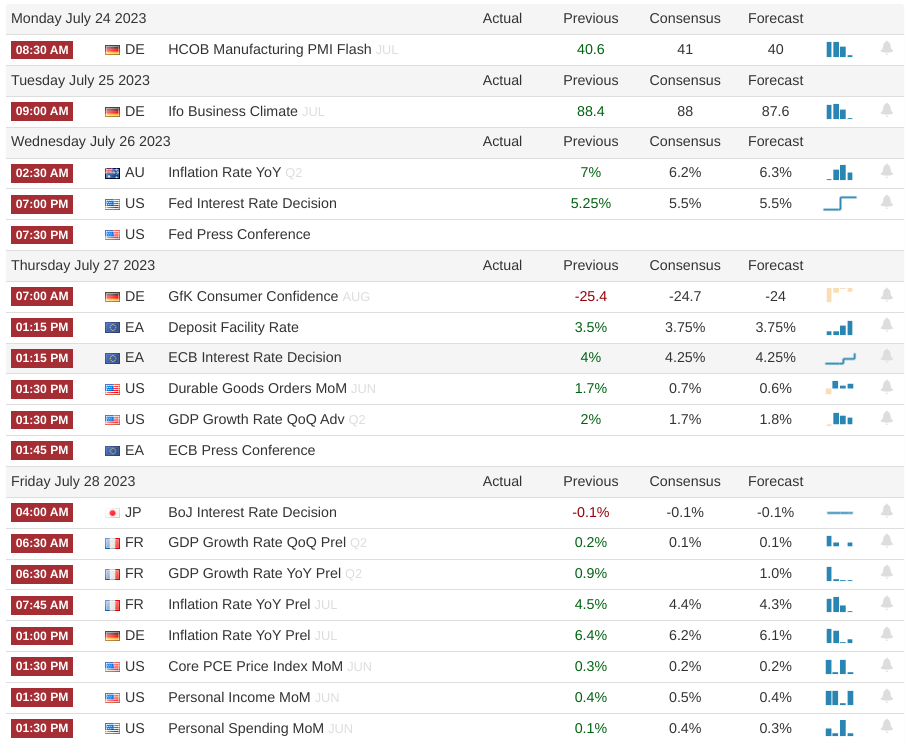
2. Week Ahead
![Obsidian Brief] When Money Becomes Software: AI, Stablecoins & Bitcoin — Implications for Sustainable and Impact Investing](/content/images/size/w720/2025/12/Gemini_Generated_Image_dppem0dppem0dppe.png)
![Leadership] AI Is Changing Everything — How a CEO Managing $1.6 Trillion Stays Ahead, ft. Jenny Johnson from Franklin Templeton](/content/images/size/w720/2025/12/Screenshot-2025-12-03-060128.png)
![AI] The Future of Work, Robotics & AI Infrastructure (Elon's bold predictions: work will be optional & currency could be irrelevant)](/content/images/size/w720/2025/11/Screenshot-2025-11-22-074621.png)